Augmented reality for order picking in warehouses
👉 THE PROBLEM
Order pickers currently use static maps and paper based maps to pick multiple orders, that accounts for 60% of operational costs in the warehouse.
📜 CONTEXT
👩 ROLE
⏱ DURATION
Lit review findings .
Current methods and associated constraints
CURRENT METHODS
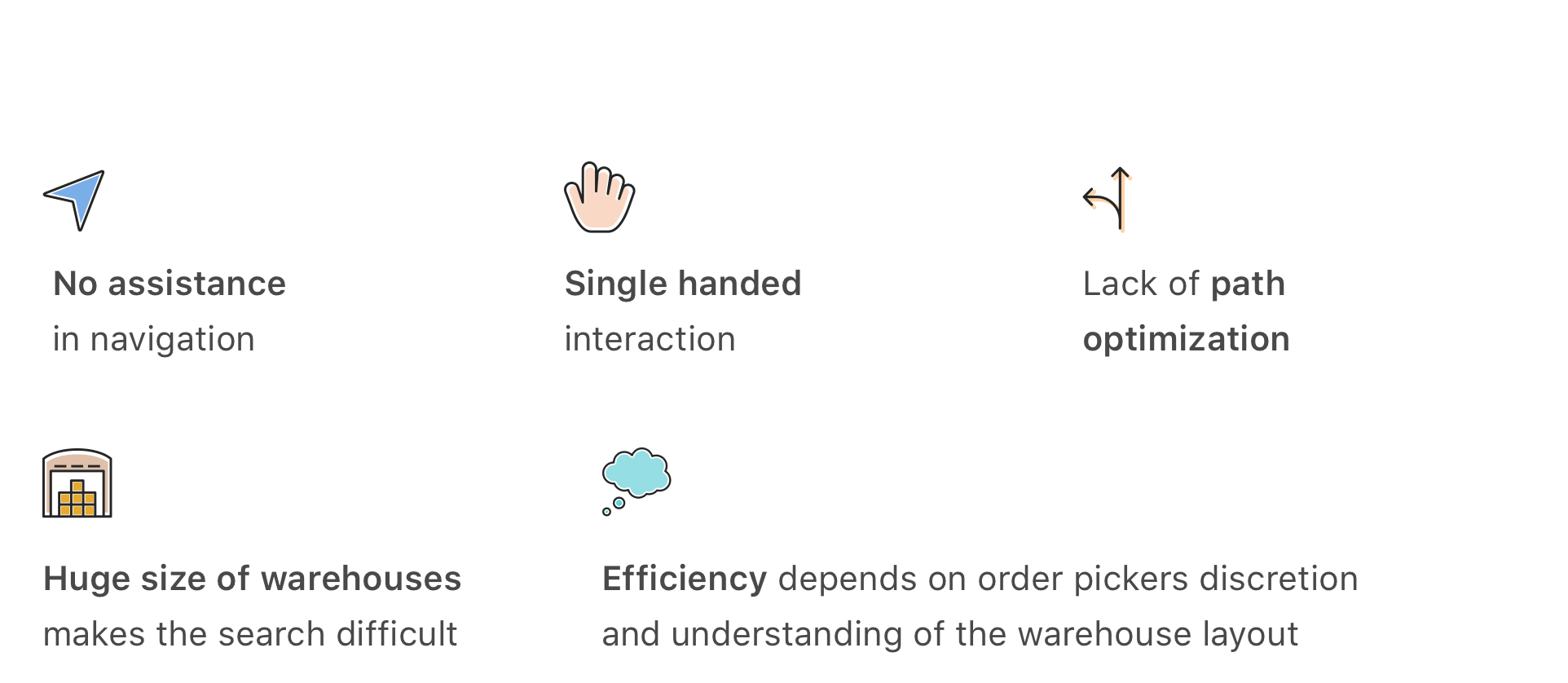
Paper based methods come with several constaints and painpoints..
The paper provides location of items using aisle and shelf numbers, which is not intuitive and requires the picker to refer back and forth to the paper.
NEED OF THE HOUR
A more time efficient and accurate order picking process is the need of the hour due to the impact that operational costs have on businesses. Such an intervention shall also decrease the fatigue of workers and hence prevent man-made errors.
PAST RESEARCH SUGGESTS..
HMDs can increase the speed of order picking by 37% compared to a paper based method. Hence, we proposed an augmented reality (AR) based solution.
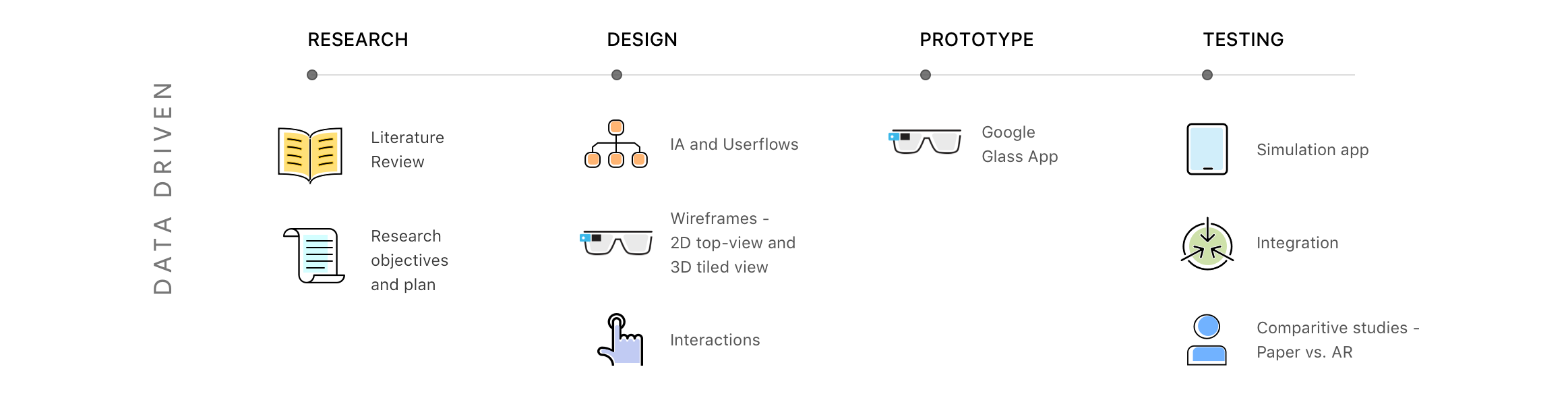
Ideation and Concept Testing .
User journeys, Idea generation and Concept Testing
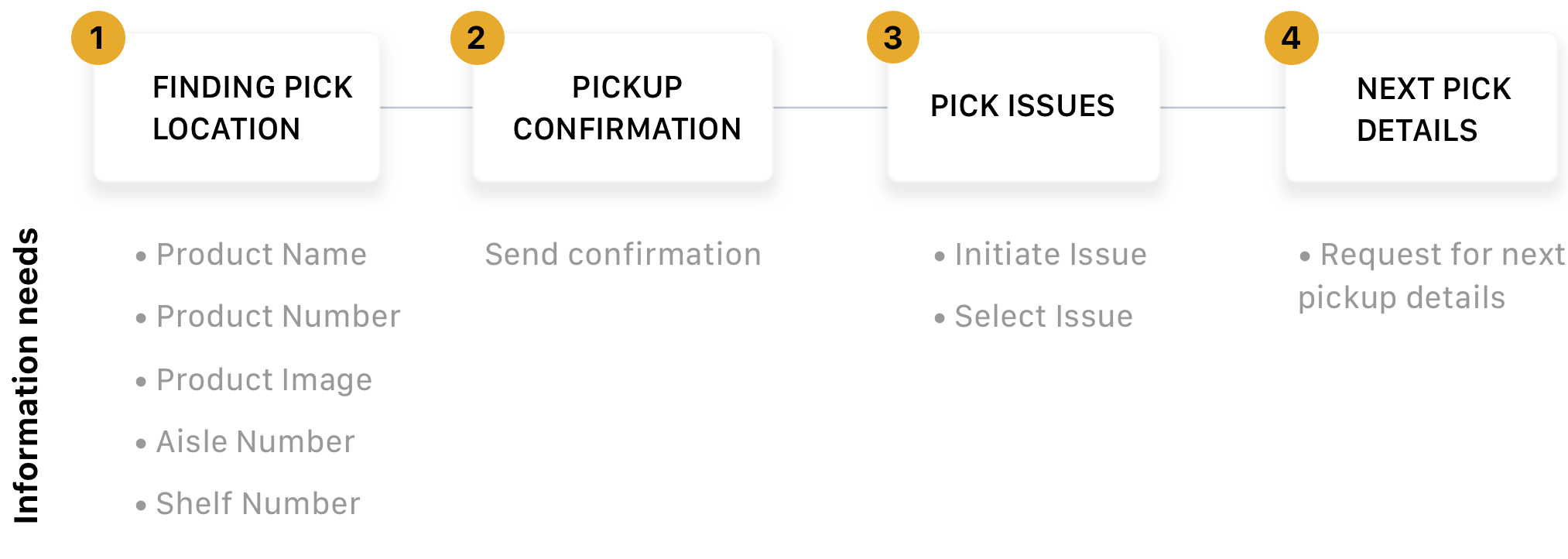
STEPS INVOLVED
Navigation to the pick location is the primary step.
The information needs associated with each step are listed beside:
GESTURES CHOSEN
3 gestures supported by Google glass were chosen.
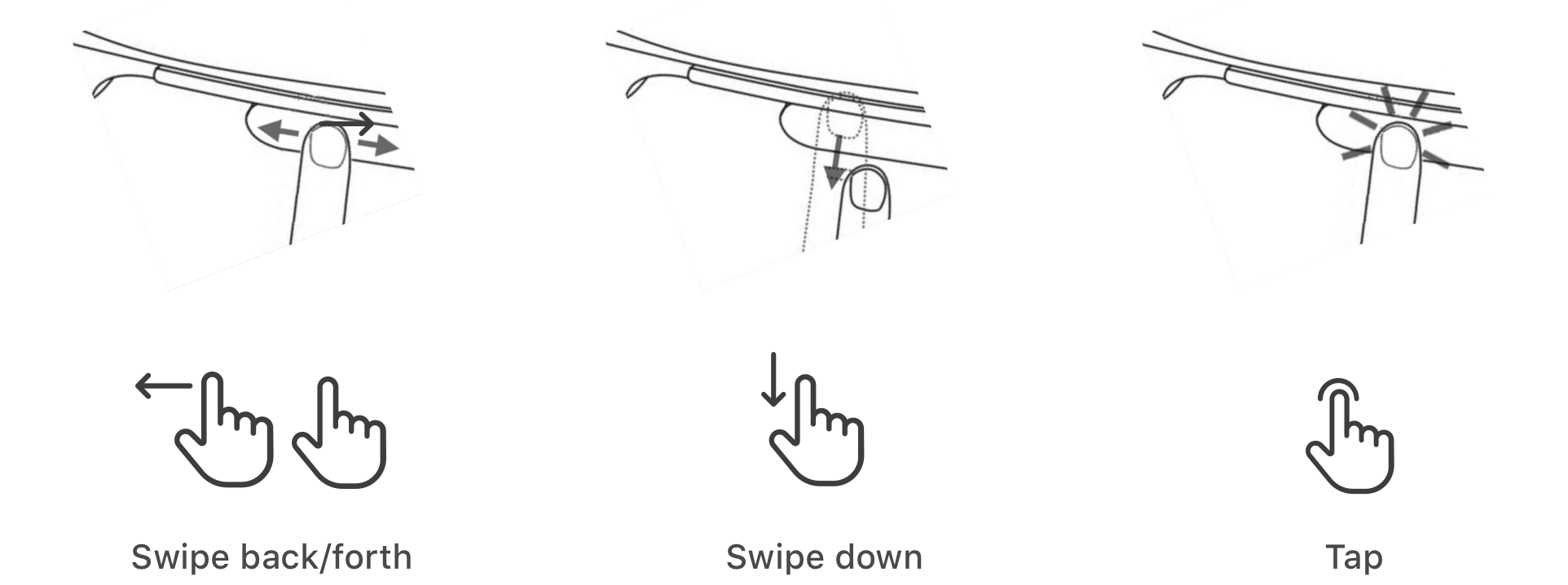
Design 1 was easier for users to comprehend.
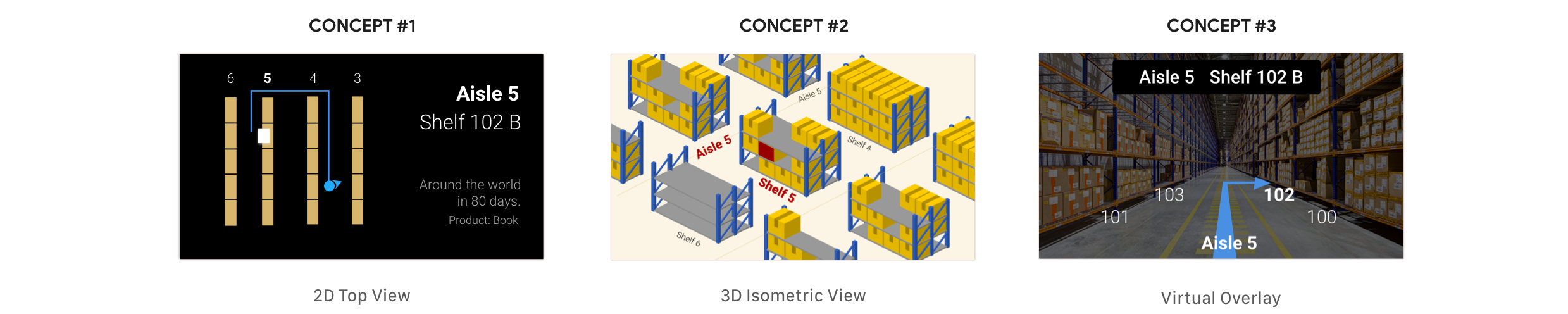
Design and Prototype .
Google glass app UI

PICK PATHS AND NAVIGATION
Pick paths are generation and navigation are automatic.
Time taken to complete a task and number of errors were measured for tasks completed by AR vs paper.

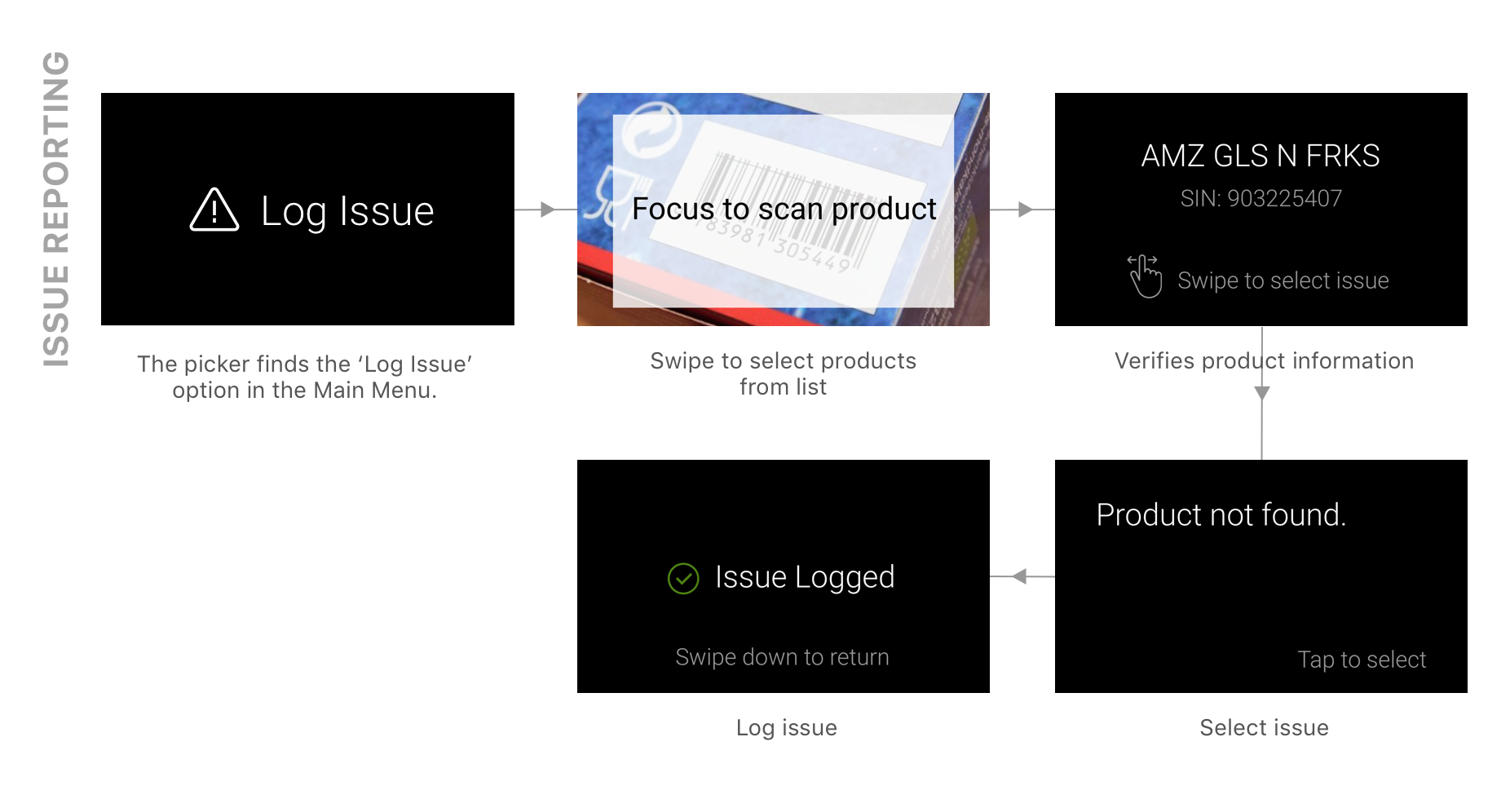
PICK REPORTING
Pickers can scan and log the picked item.
Time taken to complete a task and number of errors were measured for tasks completed by AR vs paper.

ISSUE REPORTING
Issues with products currently being picked can be reported.
Time taken to complete a task and number of errors were measured for tasks completed by AR vs paper.
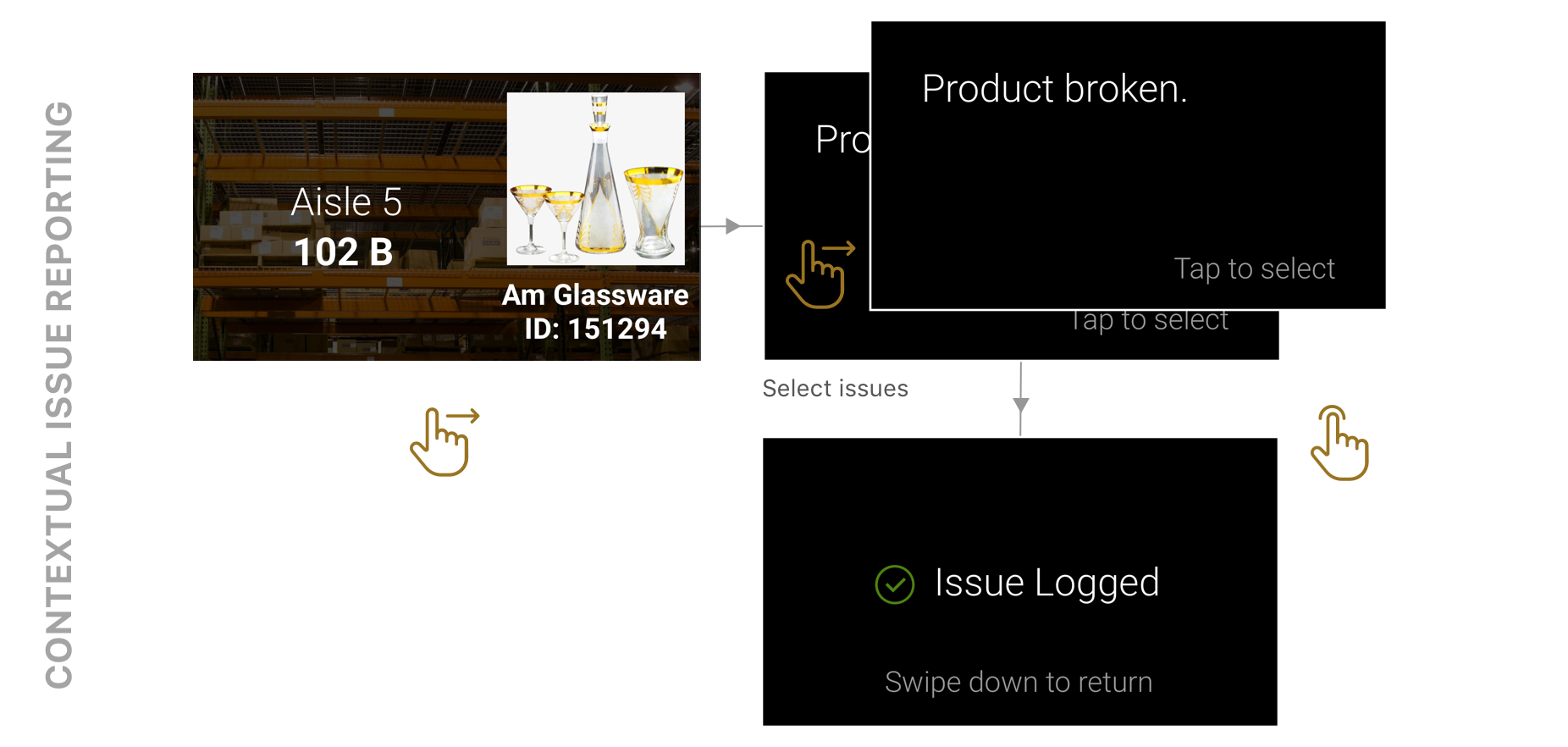
ISSUE LOGGING
Pickers can log a variety of issues by scanning products.
Time taken to complete a task and number of errors were measured for tasks completed by AR vs paper.
Usability Evaluation .
AR based order picking vs paper based order picking
WHAT DID WE MEASURE?
Accuracy and Efficiency were calculated.
Time taken to complete a task and number of errors were measured for tasks completed by AR vs paper.


Pick by Paper

Pick by AR
WHAT DID WE FIND?
AR provided better navigation cues and feedback, and caused less confusion.

HOW DID WE TEST?
Comparitive studies were conducted in a simulated warehouse environment.
Learn more about the simulation and testing process

Conclusions and Learnings .
Accuracy and Efficiency